RFID in Explosion-Hazardous Areas: Three Examples from the Field by Pepperl+Fuchs

September 7, 2022
RFID: Noncontact identification based on radio waves is considered a versatile technology and one of the keys to production environments based on the Industry 4.0 principle. The range of applications is by no means limited to discrete manufacturing—RFID is also becoming increasingly popular in process plants due to the ever more extensive requirements for marking product and work equipment. However, explosion protection requirements often have to be taken into account, because wherever flammable gases, vapors or dusts are generated, electrical equipment poses a significant safety risk. In this blog article, you will gain insight into three application examples that will help you understand the successful and safe use of RFID in hazardous areas.
1. Reliable Detection and Protection of Hose Connections Using RFID
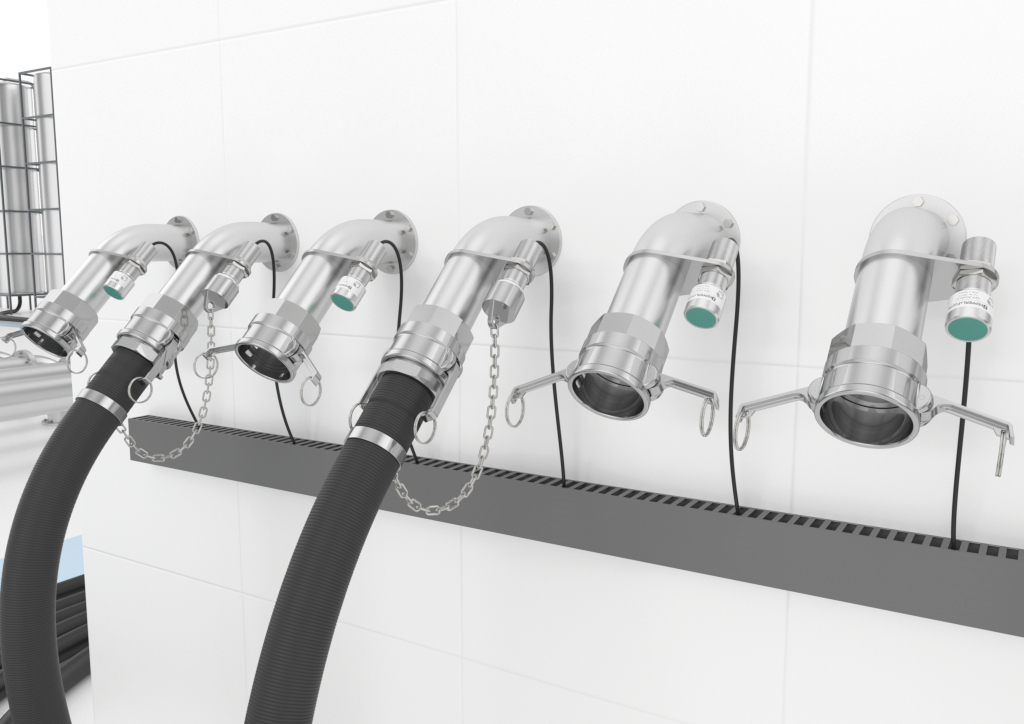

RFID read/write heads are mounted at the hose station in the immediate vicinity of the respective hose coupling
Hoses are a universal work tool in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, used to transport liquids, granules and powders. It is critical for process integrity and safety, as well as quality assurance, that hoses are connected only to their intended endpoints and that this connection is made reliably. An incorrect or unestablished connection can lead to safety problems, production downtime, significant cleaning effort or damage to the equipment with high consequential costs.
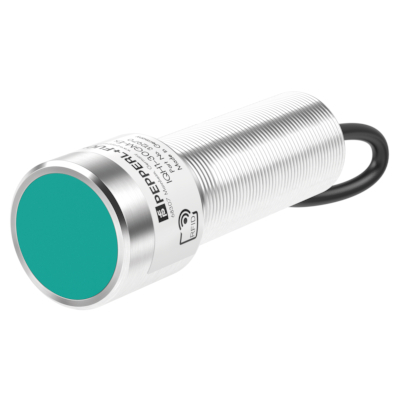

Such problems can be prevented with special RFID read/write heads in the “Ex m” type of protection (encapsulation). These devices, which are approved for applications up to ATEX Zones 1 and 21, are mounted at the hose station in the immediate vicinity of the respective hose coupling. An RFID tag attached to the hose carries the data relevant for identification, such as the hose number. Only after the control system has checked the correct assignment between hose and hose coupling does it release the subsequent process step.
RFID read/write head in “Ex m” type of protection
2. Convenient Hose Maintenance in Explosion-Hazardous Areas with RFID
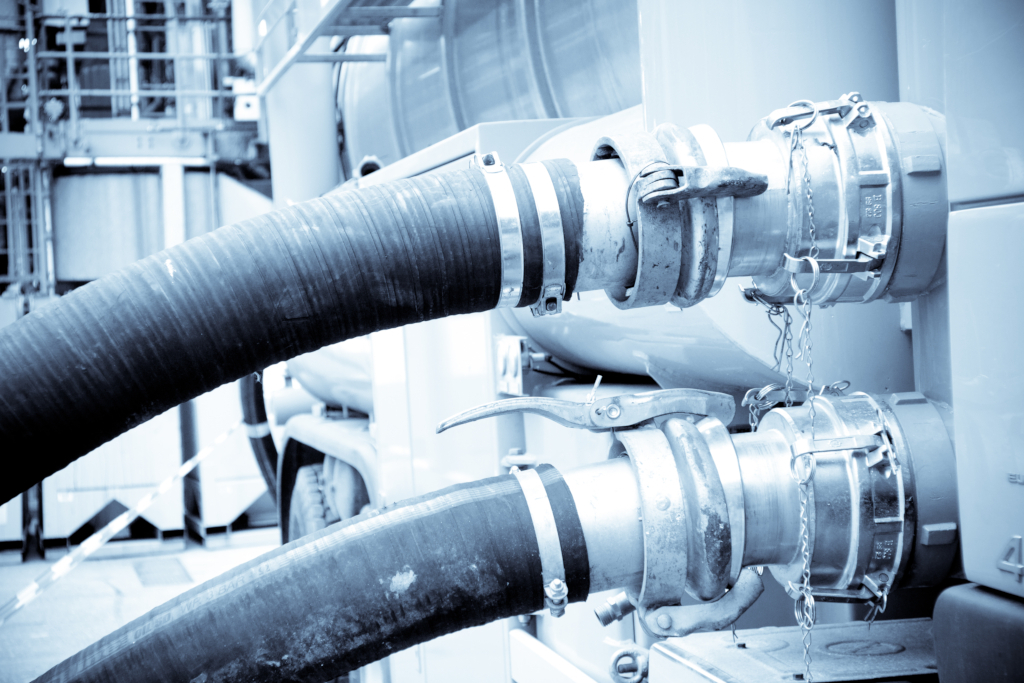

Maintenance cycles for hoses must be adhered to in order to detect signs of wear and emerging cracks or leaks
Our second application example is also dedicated to hoses in process plants. After all, not only their correct connection is crucial for the safety of processes—at the same time, legally defined maintenance cycles must be adhered to in order to detect signs of wear and emerging cracks or leaks at an early stage. However, proper maintenance requires interrupting ongoing operations, shutting down the entire plant and removing the hoses to be checked. Plant operators are therefore keen to keep further inspection work to a minimum and therefore save additional time and costs.
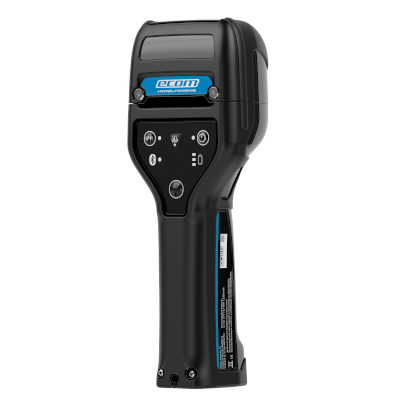

Pepperl+Fuchs offers an extremely convenient solution for this with its IoT subsidiary Neoception: Bluetooth® handhelds of the “Ident-Ex” type designed in the “Ex i” type of protection (intrinsic safety), in combination with a special software application, enable flexible hose testing in hazardous areas. With the help of the RFID handheld, the hose information (e.g., device number, test date/time or test pressure) is read out. Neoception’s integrated “hose manager” software documents the information and guides the tester step-by-step through each test. This ensures that no test step is forgotten and all results are recorded. These are then available in a report file and can be forwarded wirelessly to an ERP system. The user interface of the RFID handheld is designed to be easy to operate even when wearing gloves. In addition, mobile workers can use the handheld not only to record RFID tags, but also to read various 1-D and 2-D code symbologies.
RFID handheld in “Ex i” type of protection
3. Optimized Vehicle and Container Identification in Process Plants

RFID readers identify tags attached to tank and silo containers
Another area in which the use of RFID provides increased efficiency and safety is vehicle and driver identification in process plants. Already at the plant gate of a refinery, long-range UHF read/write heads can identify arriving vehicles and drivers without contact and check them for access authorizations and ADR tickets. This eliminates the need for drivers to leave their vehicles to make manual entries at a terminal. As a result, backlogs at peak times are avoided.

Explosionproof variants of UHF read/write heads can also be used to optimize workflows at loading stations. These devices, which are installed in enclosures with “Ex d” type of protection (flameproof enclosure), identify RFID tags attached to tank and silo containers and verify, for example, whether the correct container has been placed at the associated loading station. If the matching via the control system is successful, the responsible employee immediately receives a notification. They can then dock the container and initiate the next process steps without downtime or waiting time.
RFID reader in “Ex d” type of protection enclosure
What Does Your Use Case Look Like?
Are you also considering the integration of RFID in your process plant? Like no other supplier on the market, Pepperl+Fuchs combines decades of experience in electrical explosion protection with equally comprehensive knowledge in the development of RFID systems. In addition to UHF, our portfolio also includes LF and HF technology as well as the option of connecting to Industrial Ethernet and almost all common fieldbuses.
More Information
HF RFID Read/Write Heads in Type of Protection “Ex m”
RFID Handhelds in Type of Protection “Ex i”
UHF RFID Read/Write Heads in Type of Protection “Ex d”
Feel free to contact Pepperl+Fuchs if you need support in implementing an RFID system. Our experts look forward to your inquiry. Click here